Drones and Digital Twins: Revolutionizing 3D Mapping in Urban Areas
Drone 3D mapping involves using drones equipped with specialized cameras to capture aerial images of an area. These images are then processed using photogrammetry software to create high-resolution 3D maps and models. In recent years, the integration of drone technology with digital twin concepts has emerged as a powerful approach for 3D mapping in urban areas.
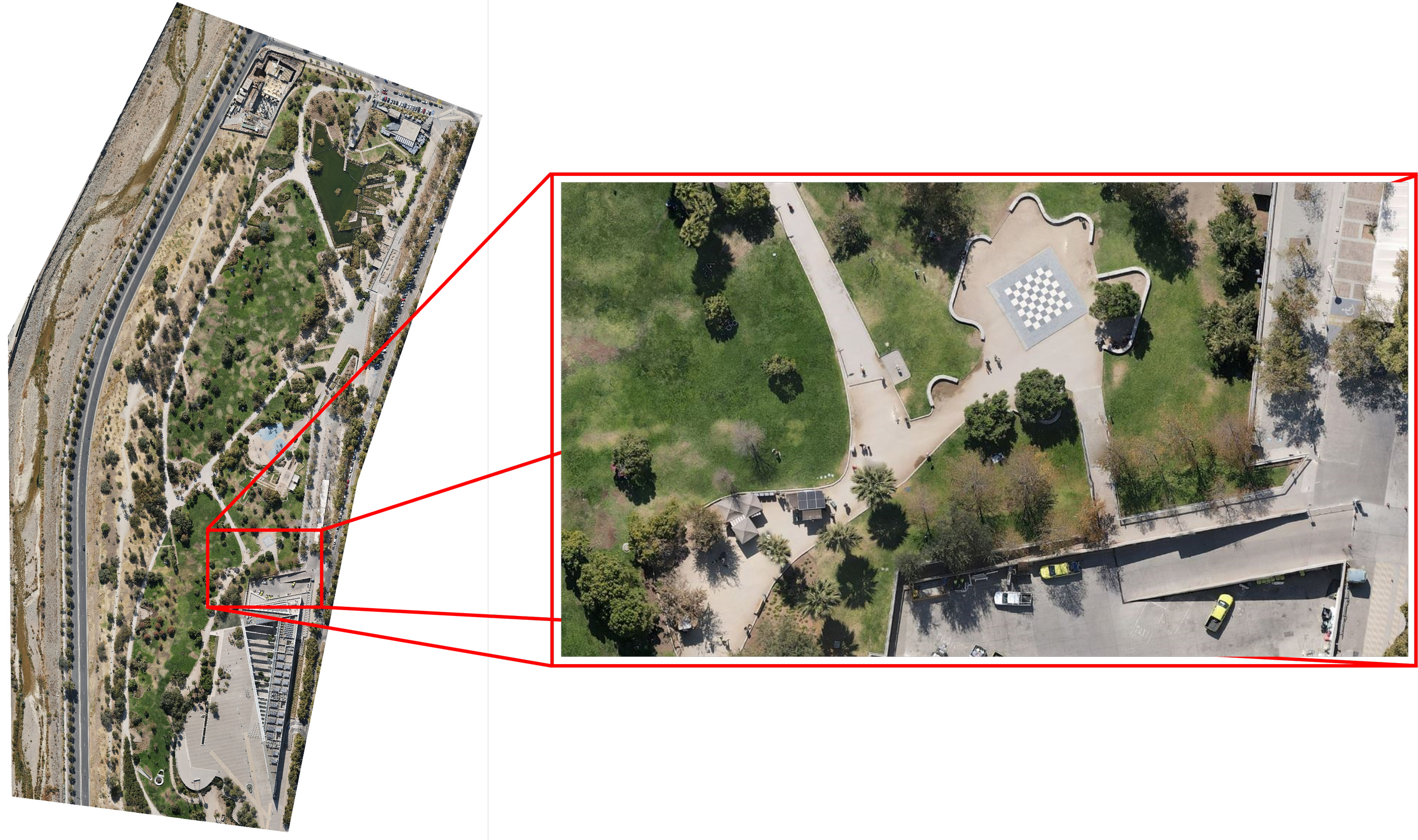
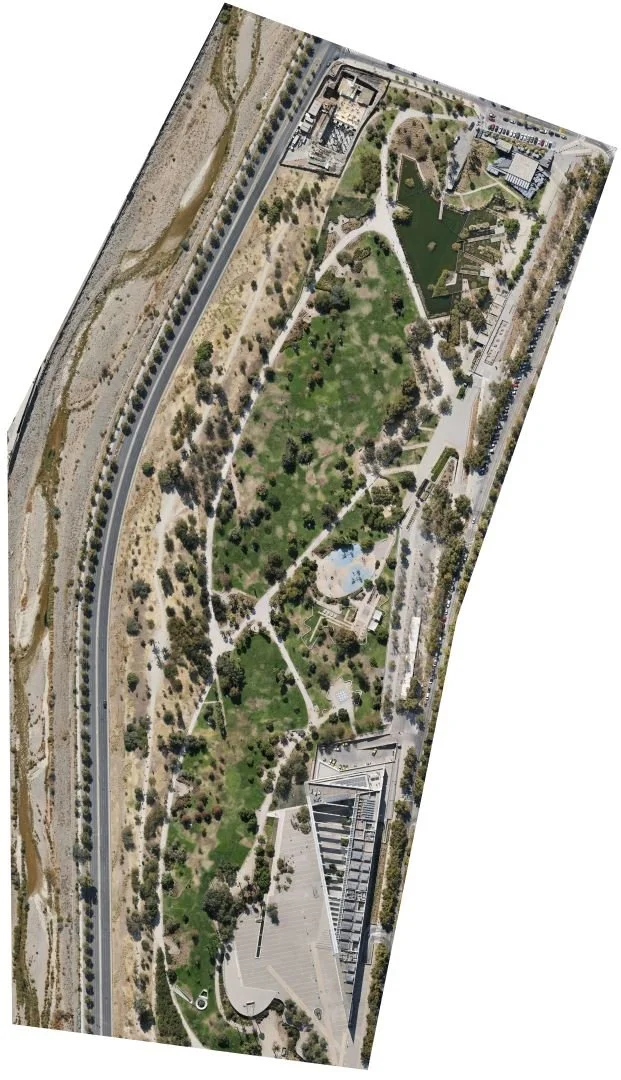
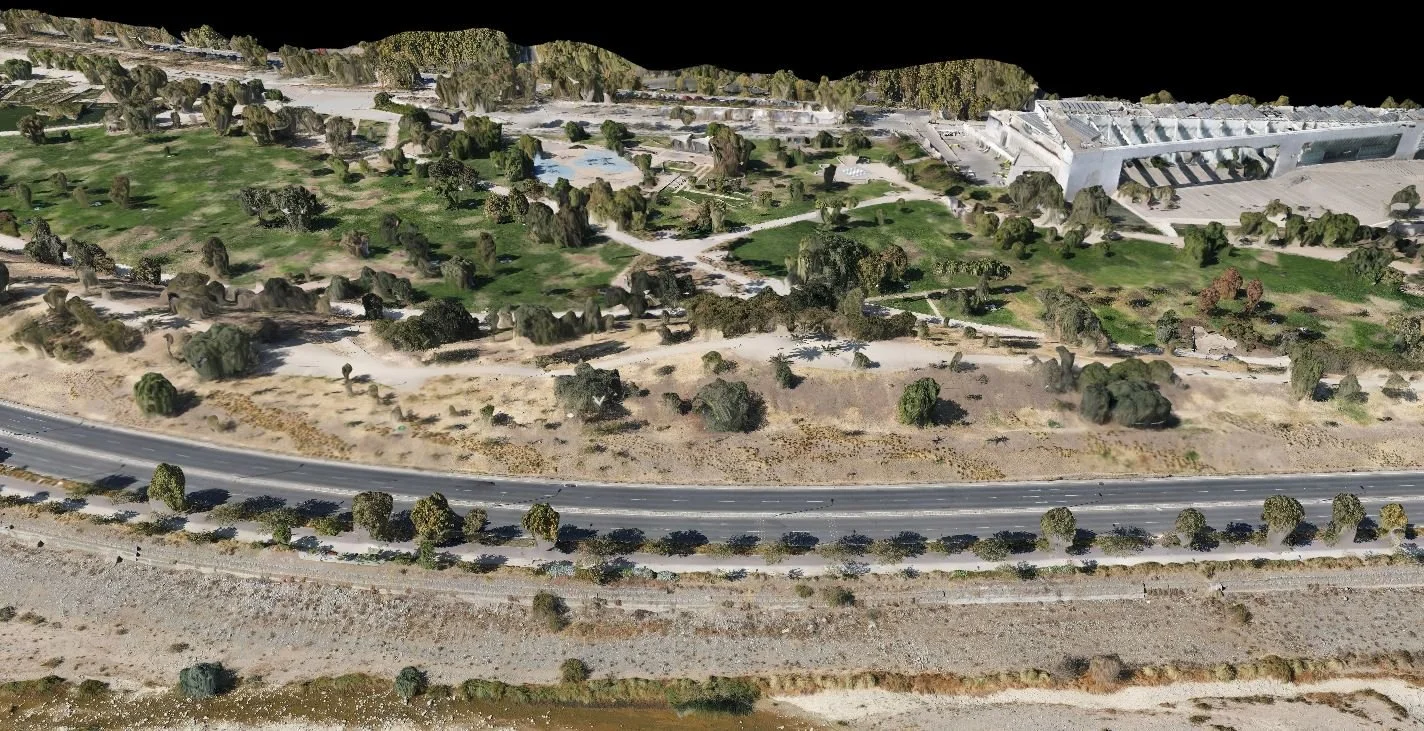
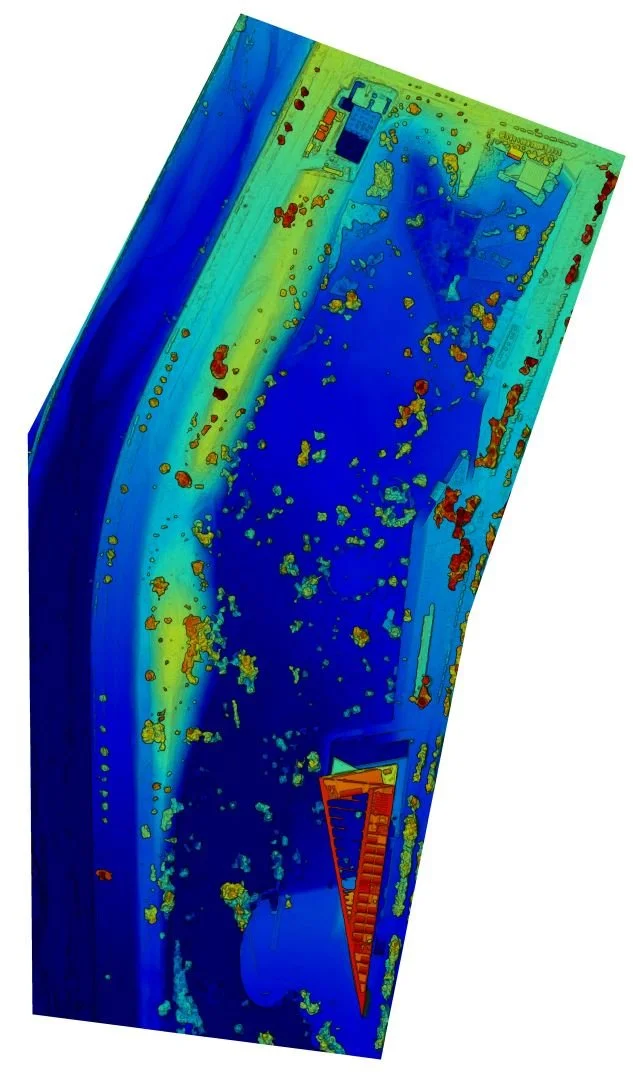
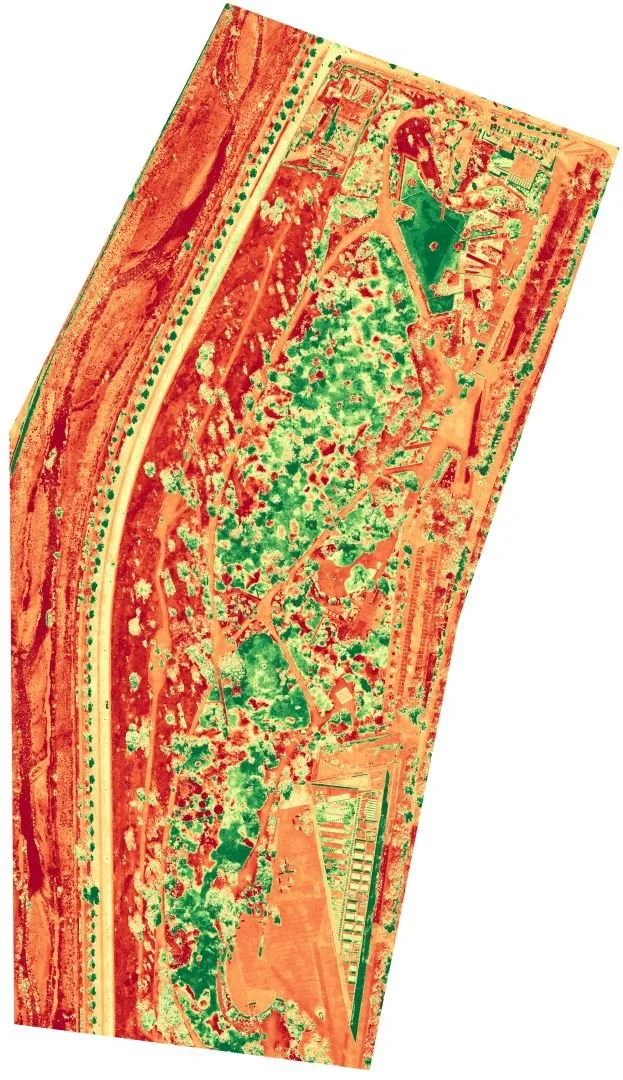
A rapid 3D site survey of Universidad del Desarrollo was conducted using a DJI Mavic Air 2 drone in April 2022.
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical object or system that is continuously updated with real-time data from sensors and other sources. This digital replica allows for the accurate simulation, monitoring, and optimization of the physical counterpart. Jeong et al. (2022) In the context of urban environments, a digital twin city is a comprehensive digital model that replicates the physical infrastructure, buildings, and other elements of a city.
One of the primary benefits of using drones in conjunction with digital twins for 3D mapping is the ability to capture detailed, high-resolution data about the urban landscape. Drones can access areas that are difficult or dangerous for traditional surveying methods, such as rooftops, bridges, and other hard-to-reach locations. The data collected by drones can then be integrated into the digital twin, creating a dynamic, virtual representation of the city that is continuously updated. (Deren et al., 2021)
Another key benefit is the digital twin's ability to facilitate proactive monitoring and maintenance of urban infrastructure. By continuously updating the digital twin with data from drones and other sensors, infrastructure managers can detect and address issues before they escalate, leading to cost savings, improved efficiency, and reduced disruptions to the city's operations. (Hakdaoui et al., 2020)
This integrated approach offers several key advantages for urban planning, infrastructure management, and emergency response. For instance, the digital twin enables different agencies to collaborate and coordinate by sharing and reviewing plans, designs, and models of various projects in the same vicinity. (Ali et al., 2023) Additionally, the digital twin can enhance emergency response capabilities by modeling and simulating crowd dispersal and establishing evacuation procedures during crises.
Moreover, the digital twin can improve transportation planning by analyzing real-time data on traffic flows and pedestrian movement patterns, allowing for optimization of infrastructure and services. A prime example is a project in Zurich that uses advanced technologies, such as sensors, drones, and 3D modeling software, to create a comprehensive digital twin of the city's physical environment.
As the development of smart cities accelerates, the use and potential of digital twins are poised to grow significantly. The increased connectivity and data collection enabled by Internet of Things technologies will further enhance the capabilities of digital twins, permitting the development of more advanced AI algorithms and simulations.
Urban pollution is a major concern in many cities, and digital twins can play a crucial role in addressing this issue. Digital twins can integrate data from air quality sensors and drones to create detailed models of air flow and pollution dispersion within the city. These simulations can help urban planners and policymakers identify the most effective strategies for improving air quality, such as implementing traffic management measures or designing green infrastructure.